Video Walkthrough
TL;DR
Salesforce Health Cloud is a powerful but expensive enterprise healthcare CRM platform, widely used by large public health organizations like the Ontario Ministry of Health. While decision-makers and procurement teams approve of its capabilities, frontline healthcare workers struggle with cumbersome workflows, slow performance, and data integration issues, notably the inability to sync pharmacy vaccine records with ministry databases. The tool’s complexity fuels an ecosystem of specialists to maintain and support it, but real user experience suffers. This analysis proposes a ground-up improvement approach that prioritizes usability, data integration, and frontline efficiency, rather than catering solely to the purchasing stakeholders.
Introduction to a large healthcare CRM
Salesforce Health Cloud is an enterprise-grade software widely used by major healthcare organizations, including the Ontario Ministry of Health and its associated public health bodies such as Toronto Public Health and Peel Region. Designed to offer a comprehensive patient management system, the platform boasts an extensive feature set but comes with a high cost of ownership and maintenance, supporting an entire ecosystem of specialists dedicated to its implementation, support, and customization. Despite its enterprise adoption, the tool struggles with interoperability, making data integration with other Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems problematic. A notable example is the failure to sync pharmacy vaccine records with ministry databases, forcing patients through bureaucratic hurdles to obtain a complete view of their own health data.
On the front lines, healthcare professionals widely criticize the tool for its cumbersome data entry workflows, slow performance, and unreliable local caching, which sometimes leads to patient data loss. Meanwhile, procurement teams and political decision-makers, who oversee its adoption, rarely face these operational challenges and remain largely satisfied with vendor relationships and IT contract negotiations. This analysis presents a ground-up approach to improving Salesforce Health Cloud—not for the purchasing stakeholders, but for the real users who rely on it daily. By addressing usability concerns, data integration gaps, and frontline frustrations, the platform can evolve from a bureaucratic necessity into a true enabler of modern healthcare delivery.
A one-page walkthrough of the product
Salesforce Health Cloud is a comprehensive patient and member relationship management platform designed to provide healthcare organizations with a 360-degree view of their patients. By integrating clinical and non-clinical data, it enables personalized engagement, efficient care coordination, and improved health outcomes.
- Unified Patient Profiles: Consolidates data from various sources to create a comprehensive view of each patient, including medical history, appointments, and communication records.
- Care Plan Management: Allows healthcare providers to develop, monitor, and adjust individualized care plans, ensuring patients receive tailored care.
- Secure Communication: Facilitates HIPAA-compliant messaging between care teams and patients, enhancing collaboration and patient engagement.
- Integration Capabilities: Seamlessly integrates with Electronic Health Records (EHRs) and other healthcare systems, ensuring data consistency and accessibility.
- Analytics and Reporting: Offers robust tools for tracking patient outcomes, operational efficiency, and other key performance indicators.
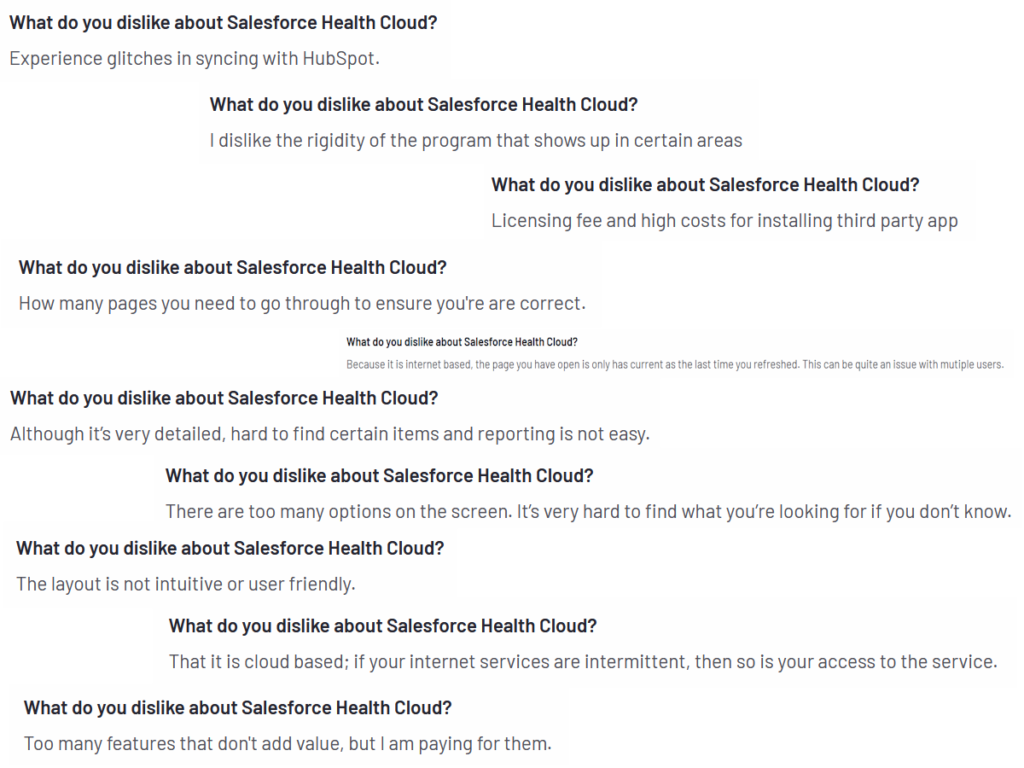
Based on publicly available reviews, Salesforce Health Cloud has received mixed feedback:
Positive Aspects:
- Comprehensive Data Management: Users appreciate the platform’s ability to consolidate patient information, making it easier to access and manage data.
- Customization and Flexibility: The platform’s adaptability to various healthcare workflows is frequently highlighted.
Areas for Improvement:
- Complexity and Learning Curve: Some users find the platform complex, requiring significant time to master.
- Cost Considerations: The pricing is noted as a barrier for smaller healthcare organizations.
- User Interface: Feedback indicates that the interface could be more intuitive and modernized.
A. User-Centric Approach
- Primary Users: Healthcare providers, administrative staff, and care coordinators seeking efficient patient management tools.
- Challenges:
- Usability: The platform’s complexity may hinder user adoption.
- Affordability: High costs could limit accessibility for smaller practices.
B. Big Picture View
- Market Context: The demand for integrated healthcare solutions is rising, driven by the need for coordinated care and regulatory requirements.
- Strategic Positioning: Salesforce Health Cloud positions itself as a versatile solution capable of adapting to diverse healthcare needs.
C. Iterative and Evidence-Based Development
- Feedback Integration: Regularly updating the platform based on user feedback can enhance usability and satisfaction.
- Metrics to Monitor:
- User Adoption Rates
- Customer Satisfaction Scores
- Operational Efficiency Improvements
D. Business Viability
- Revenue Model: Subscription-based pricing may be prohibitive for smaller organizations. Exploring tiered pricing or modular offerings could broaden the customer base.
- Cost Management: Balancing feature development with affordability is crucial to maintain competitiveness.
E. Collaboration Across Teams
- Internal: Aligning product development with sales and customer support to ensure cohesive strategy execution.
- External: Partnering with EHR providers and other healthcare technology vendors to enhance integration capabilities.
An examination of Salesforce’s recent quarterly reports and product release notes indicates ongoing efforts to address some of the identified areas:
- Usability Enhancements: Recent updates have focused on improving user experience, such as introducing AI-generated summaries and emails to boost productivity.
- Feature Expansion: The platform has added new visual displays and data management tools to bring users closer to their patients and salespeople.
- Security Improvements: Enhancements have been made to protect sensitive information by verifying the identity of callers, thereby expanding support for patient safety and privacy.
- Enhance User Training: Develop comprehensive onboarding programs to reduce the learning curve and improve user adoption.
- Revise Pricing Strategy: Consider flexible pricing models to make the platform more accessible to smaller healthcare providers.
- Modernize User Interface: Invest in UI/UX improvements to create a more intuitive and visually appealing interface.
- Expand Integration Partnerships: Broaden integration capabilities with various EHR systems to enhance data interoperability.